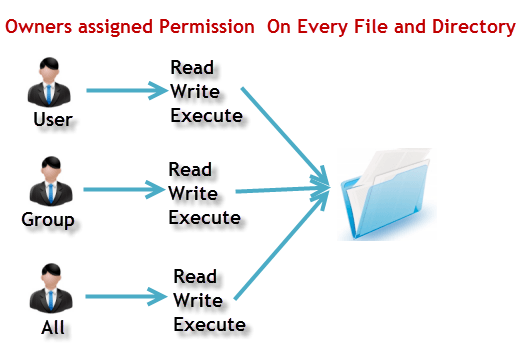
✔️Linux File Permissions:
Every file and directory in your UNIX/Linux system has following 3 permissions
Read: This permission give you the authority to open and read a file. Read permission on a directory gives you the ability to lists its content.
Write: The write permission gives you the authority to modify the contents of a file. The write permission on a directory gives you the authority to add, remove and rename files stored in the directory. Consider a scenario where you have to write permission on file but do not have write permission on the directory where the file is stored. You will be able to modify the file contents. But you will not be able to rename, move or remove the file from the directory.
Execute: In Windows, an executable program usually has an extension “.exe” and which you can easily run. In Unix/Linux, you cannot run a program unless the execute permission is set. If the execute permission is not set, you might still be able to see/modify the program code(provided read & write permissions are set), but not run it.
✔️Changing file/directory permissions in Linux Using ‘chmod’ command :
syntax: chmod permissions filename
There are 2 ways to use the command –
Absolute mode
Symbolic mode
✔️Absolute mode:
in this mode, file permissions are not represented as characters but a three-digit octal number.
The table below gives numbers for all for permissions types.
| Number | Permission Type | Symbol |
| 0 | No Permission | — |
| 1 | Execute | –x |
| 2 | Write | -w- |
| 3 | Execute + Write | -wx |
| 4 | Read | r– |
| 5 | Read + Execute | r-x |
| 6 | Read +Write | rw- |
| 7 | Read + Write +Execute (all permission) | rwx |
Let's see an example of absoute mode :
if it a file has 764 permission then ,
Owner can read, write and execute.
Usergroup can read and write.
all others can only read.
.png)
This is shown as -rwxrw-r–
✔️Symbolic Mode in Linux:
In the Absolute mode, you change permissions for all 3 owners. In the symbolic mode, you can modify permissions of a specific owner. It makes use of mathematical symbols to modify the Unix file permissions.
| Operator | Description |
| + | Adds a permission to a file or directory. |
| – | Removes the permission. |
| \= | Sets the permission and overrides the permissions set earlier. |
The various owners are represented as –
u | user/owner |
g | group |
o | other |
a | all |
✔️Some other basic commands:
Command | Example | Description |
history |
| displays all commands used previously in the terminal. |
cat >> |
| used to append or add content to an already existing file. |
head -n |
| displays starting 'n' lines from the file |
tail -n |
| displays bottom 'n' lines from the file |
diff |
| shows the differences in 2 files |
Thank you so much for reading
Follow me at LinkedIn to see interesting posts like this : )

